What is an electric Field?
Definition
An electric field is a region around a charged particle where an electric force is exerted on other charged particles.
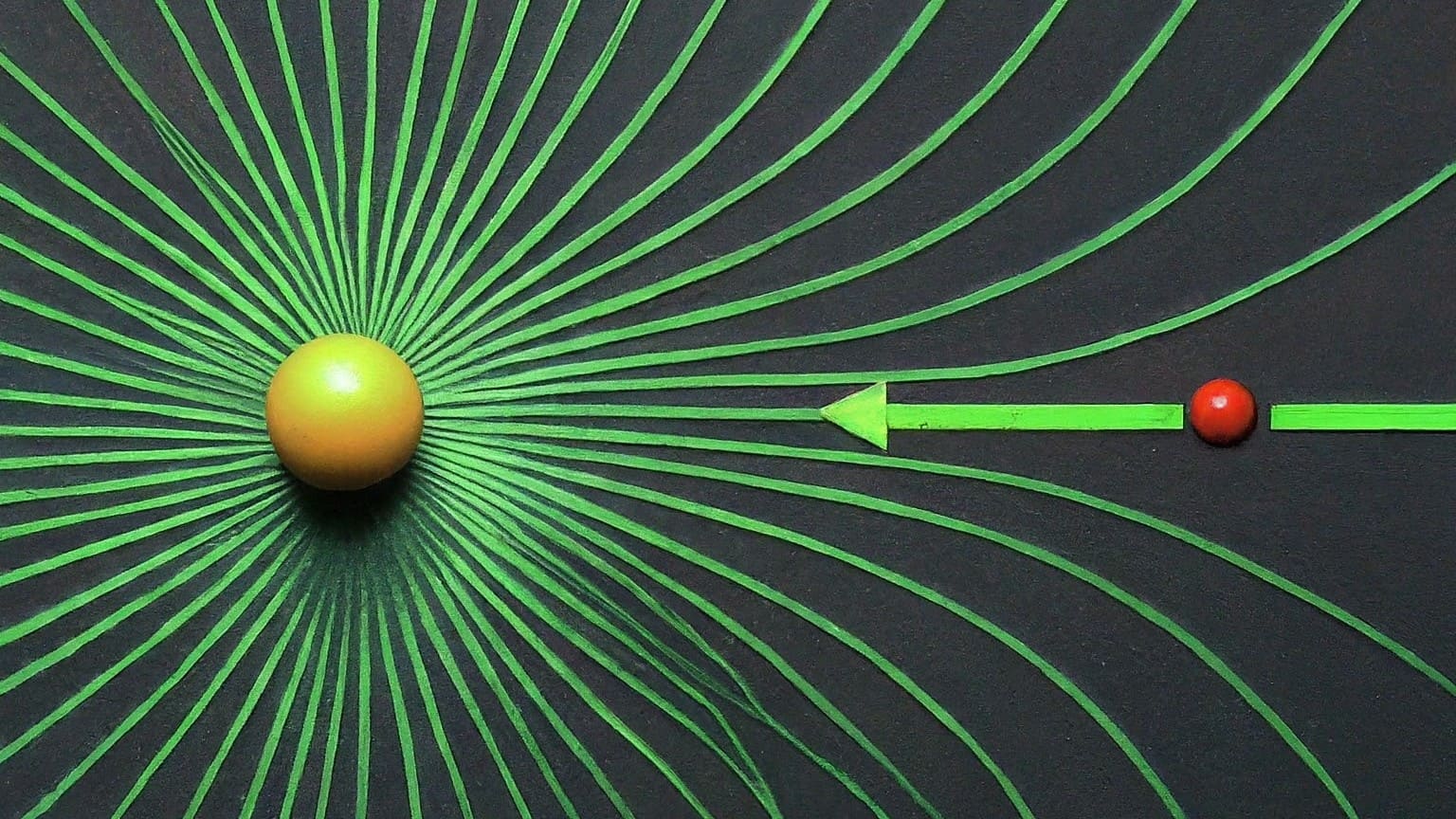
Formula
E=Kq / r
Where
Q is the charge,
r is the distance
Units
The SI unit of the electric field is Newton/coulomb.
Newton per Coulomb (N/C)- this unit comes from the formula E=F/q. It is a primary unit of electric field strength in the International System of Units (SI).
Kilovolt per Meter (kV/m) - this is another unit of electric field strength, It’s represents the electric potential difference of one kilovolt (1000 volts) over a distance of one meter and commonly used in practical applications, especially in high-voltage engineering.
Statvolt per Centimeter (statV/cm)- this unit is used in the CGS (centimeter-gram-second) system of units. It represents the electric potential difference of one statvolt over a distance of one centimeter.
Megavolt per Meter (MV/m)- this unit of electric field strength is used in high-voltage applications, such as in power transmission.
Summary of Electric Field Units
| Unit | Definition | Relationship to N/C |
|---|---|---|
| N/C (Newton per coulomb) | SI unit, force per unit charge | 1 N/C=1 N/C |
| kV/m (Kilovolt per meter) | 1 kV over 1 meter | 1 kV/m=1000 N/C |
| statV/cm (Statvolt per centimeter) | cgs unit, 1 statV over 1 cm | 1 statV/cm ≈ 29979 N/C |
| MV/m (Megavolt per meter) | 1 MV over 1 meter | 1 MV/m=1,000,000 N/C |
How to calculate Electric Field
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Electric Field
1. Point Charge
Formula:E=ke* q / r2
Steps:
- Identify the charge (q):Determine the magnitude and sign of the point charge.
- Determine the distance (r):Measure the distance from the point charge to the point where you want to calculate the electric field.
- Use Coulomb's constant (ke):ke=8.99 × 109Nm2/C2.
- Calculate the electric field (E):Plug the values into the formula to find the electric field strength.
Example:
- Charge (q)=2 × 10-6C
- Distance (r)=0.5 m
- E=8.99 × 109× 2 × 10-6/ (0.5)2
- E=7.19 × 104N/C
2. Continuous Charge Distribution
Formula (for a line charge):E=keλ / r
Steps:
- Identify the linear charge density (λ):Determine the charge per unit length.
- Determine the distance (r):Measure the perpendicular distance from the line charge to the point where you want to calculate the electric field.
- Use Coulomb's constant (ke):
- Calculate the electric field (E):
Example:
- Charge density (λ)=3 × 10-6C/m
- Distance (r)=0.2 m
- E=8.99 × 109× 3 × 10-6/ 0.2
- E=1.35 × 105N/C
3. Electric Field Between Parallel Plates
Formula:E=V / d
Steps:
- Identify the potential difference (V):Determine the voltage applied across the plates.
- Determine the distance (d):Measure the distance between the two plates.
- Calculate the electric field (E):
Example:
- Voltage (V)=12 V
- Distance (d)=0.01 m
- E=12 / 0.01
- E=1200 V/m
4. Using Gauss's Law
Formula:∮ E ⋅ dA=Qenc/ ε0
Steps:
- Select a Gaussian surface:Choose a surface that simplifies the calculation (e.g., spherical, cylindrical).
- Determine the enclosed charge (Qenc):Calculate the total charge inside the Gaussian surface.
- Use the permittivity of free space (ε0):ε0=8.85 × 10-12C2/Nm2.
- Apply Gauss's Law:Integrate the electric field over the Gaussian surface to solve for E.
Example (spherical symmetry):
- Charge (Qenc)=1 × 10-6C
- Radius of Gaussian surface (r)=0.3 m
- E ⋅ 4π r2=Qenc/ ε0
- E ⋅ 4π (0.3)2=1 × 10-6/ 8.85 × 10-12
- E=1 × 10-6/ (4π (0.3)2× 8.85 × 10-12)
- E ≈ 9.42 × 103N/C
5. Electric Field from Force and Charge
Formula:E=F / q
Steps:
- Identify the force (F):Determine the magnitude and direction of the force acting on the charge.
- Identify the charge (q):Determine the magnitude of the charge experiencing the force.
- Calculate the electric field (E):Divide the force by the charge.
Example:
- Force (F)=5 N
- Charge (q)=2 × 10-6C
- E=5 / 2 × 10-6
- E=2.5 × 106N/C
How to use an online electric field calculator
Follow these steps
- In "Enter Charge (Q)" type the value of the electric charge (Q) and then select the units for charge from the dropdown unit menu.
- In "Enter Distance (r)" type the value of the distance (r) and then select the units for charge from the dropdown unit menu.
- Click the "Calculate Electric Field" button.
- The calculated electric field (E) will appear in the "Electric Field (E)=" field.
- You can change the unit for the force from the dropdown menu it will update the result in real-time.
- To clear the input fields and start a new calculation, click the "Clear" button.
Conclusion
In this article, you learn what is the electric field, its definition, and how to calculate the electric field. Simply you have to remember that formula. Also, you can use electric field calculation for further online calculation.